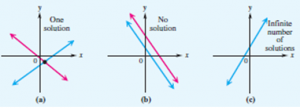
Graphs of Linear Systems in Two Variables
a. The two graphs intersect in a single point. The coordinates of this point give the only solution of the system. In this case the system is consistent, and the equations are independent. This is the most common case. See figure (a).
b. The graphs are parallel lines. In this case the system is inconsistent; that is, there is no solution common to both equations of the system, and the solution set is Ø . See Figure (b).
c. The graphs are the same line. In this case the equations are dependent, since any solution of one equation of the system is also a solution of the other. The solution set is an infinite set of ordered pairs representing the points on the line. See Figure (c).